Supply and Demand Trading in 2026
We have been trading supply and demand strategies for over ten years, and they have stood the test of time remarkably well. Supply and demand is...
The Bollinger Bands® indicator is among the most reliable and powerful trading indicators traders can choose from. Bollinger Bands® can be used to read the trend strength, to time trade entries, ride trending markets, and find potential market tops for reversal trading. The Bollinger Band® indicator is not a lagging indicator because it adjusts to price action in real-time and the indicator uses the price volatility to adjust to the current price behavior.
In this article, we show you how to use the Bollinger Bands ® indicator to improve your chart reading skills and how to identify high-probability trade entries.
We do not want to get too technical in this article, but understanding the basic premise of the indicator will help us use the indicator more effectively. If you are not interested in the underlying principles of the Bollinger Bands® indicator, you can skip ahead to the next section where we cover some common use cases.
As the name implies, Bollinger Bands® are price channels (bands) that are plotted above and below the price action.
The outer Bollinger Bands® are based on price volatility, which means that they expand when the price fluctuates and trends strongly. Conversely, the bands contract during sideways consolidations and low momentum trends. The longer the candles and the candlestick wicks, the higher the volatility is and, therefore, the further apart the Bollinger Bands® are going to be.
An important component of the Bollinger Bands ® is the standard deviation. Without getting too technical, the standard deviation measures the price fluctuation and the deviation from the average candle size.
A small standard deviation means that the candle's size was close to the average candle size. A large standard deviation means the candles' size was all over the place and deviated strongly from the usual average candle size.
The Bollinger Bands ® indicator makes use of two concepts from statistics, the so-called confidence interval, and the normal distribution. By default, the Bollinger Bands ® are set to 2 standard deviations. With a standard deviation of 2, we would say that 95% of all observed price points should fall within the Bollinger Bands®. The graph below shows a normal distribution graph with the standard deviations at the bottom x-axis.
Again, I do not want to get too technical, but a small excursion is important to understand the approach of the Bollinger Bands® indicator and why it is so powerful.
When you hear someone say "95% confidence interval," it means they're pretty certain (95% sure, to be exact) that the average price candle will fall within the range of the Bollinger Bands ®. If you're 95% sure the price will stay within the Bollinger Bands ®, you can be confident about the price prediction.
In simple terms, we would say that 95% of all the price action happens in between the Bollinger Bands®. A move outside of the outer Bollinger Bands ® shows a significant price move and is a 5% outlier.
The center of the Bollinger Bands ® is the 20-period moving average and the perfect addition to the volatility-based outer bands, especially when we start using Bollinger Bands ® for trend-following trading.
Bollinger Bands ® do not lag (as much) because they always change automatically with the price action.
We can use the Bollinger Bands ® to analyze the strength of trends and get a lot of important information this way. There are just a few things you need to pay attention to when it comes to using Bollinger Bands ® to analyze trending markets and price action:
In the following, we will examine each Bollinger Bands ® signal individually to get a better understanding of how to use the Bollinger Bands ® in our trading.
We are starting with the Bollinger Bands ® contraction because a contraction often foreshadows a trend change or a trend continuation and is, therefore, the first important signal.
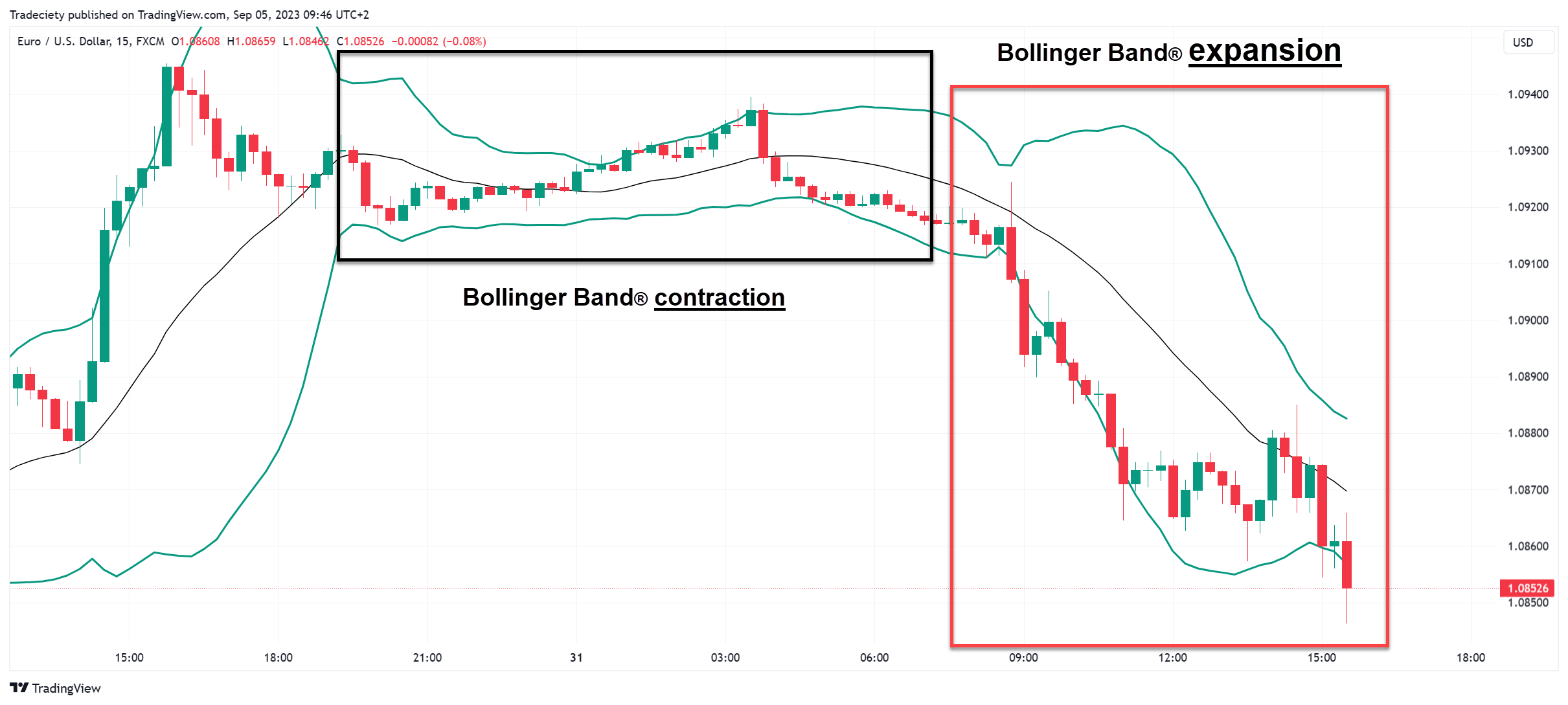
In the screenshot below, we can see that the price was in an uptrend first and then started moving sideways. During the sideways period, the candlesticks became smaller and the Bollinger Bands ® started narrowing. Especially long contraction periods can be important signals.
After the strong breakout from the contraction, the Bollinger Bands ® started widening immediately, signaling the strong trending price action. During trending markets, when the price pushes into one direction with long candlesticks, the Bollinger Bands ® widen, confirming the high level of volatility – a deviation from the normal price behavior.
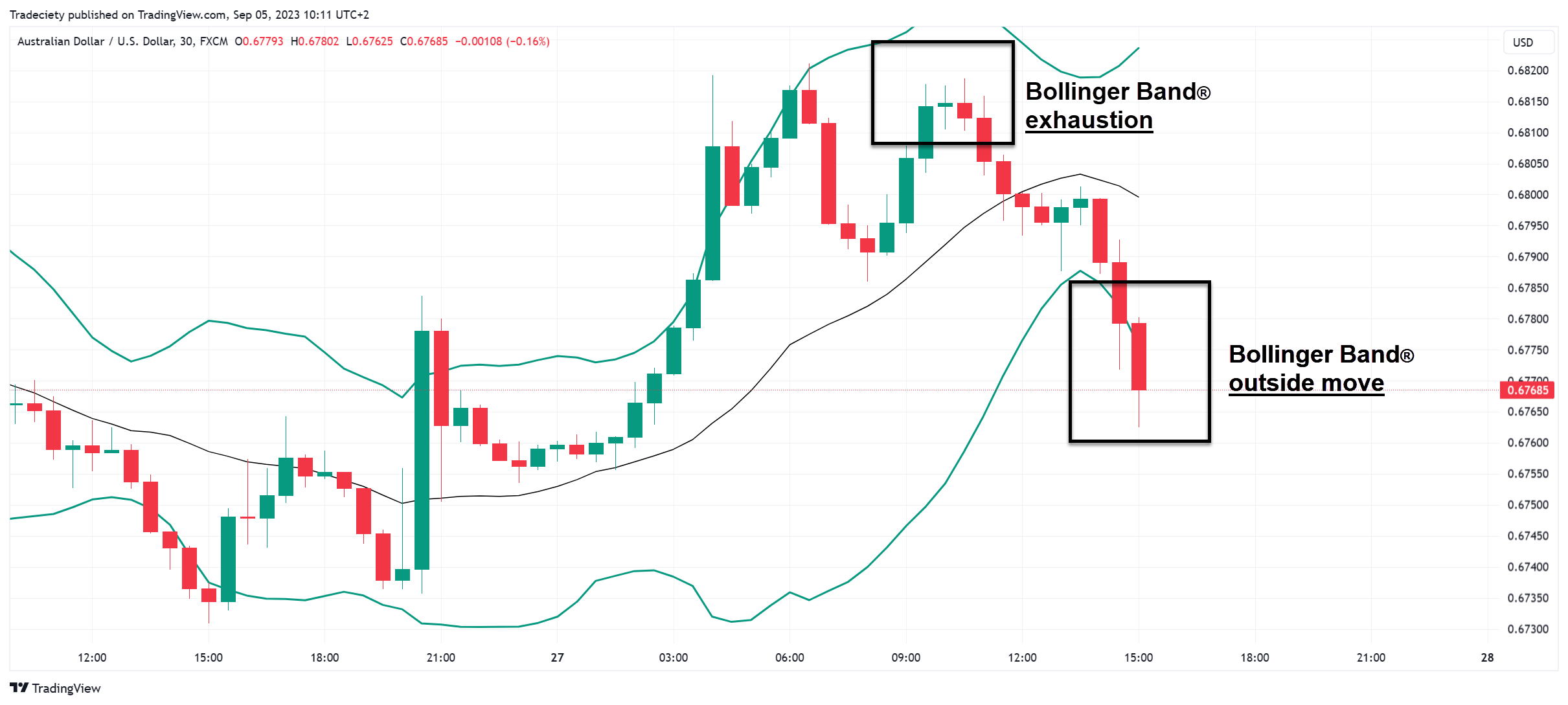
In the screenshot below, the price first showed a Bollinger Bands ® exhaustion. The exhaustion is confirmed when the price fails to reach the upper Bollinger Bands ® in an uptrend. Whereas previously in the uptrend, the price was able to reach and trade outside the upper band, during the exhaustion, the price could not continue the trending phase. This is the first sign of a trend reversal.
Next, the price moved all the way into the opposite Bollinger Bands ® and started trading outside the lower band. The price showed extreme strength and the price was even able to close outside the lower band. As we have learned, most of the candlesticks will fall inside the Bollinger Bands ®. A move outside the bands shows, therefore, extreme trend strength.
After the push outside the lower Bollinger Bands ®, the trend continued to the downside and the price stayed very close to the lower band. Strong continuation pushes below the lower band confirm the trend direction.
Finally, the Bollinger Bands ® started contracting and the bands narrowed when the price started moving sideways with smaller candlesticks. A bullish trend change might now be underway when the price starts pushing into the upper Bollinger Bands ®.
So far, we have seen that breakouts from contractions can foreshadow new trending phases and a strong push outside of the Bollinger Bands ® can be seen as a trend confirmation. But the Bollinger Bands ® indicator can also be used for trend-following pullback trading. Once a trend is on its way, traders typically wait for the price to show a pullback phase. A pullback is a short pause in the trending market where the price moves sideways or makes a short move into the opposite trend direction. Evaluating the pullback phases can tell traders a lot about the underlying trending dynamic.
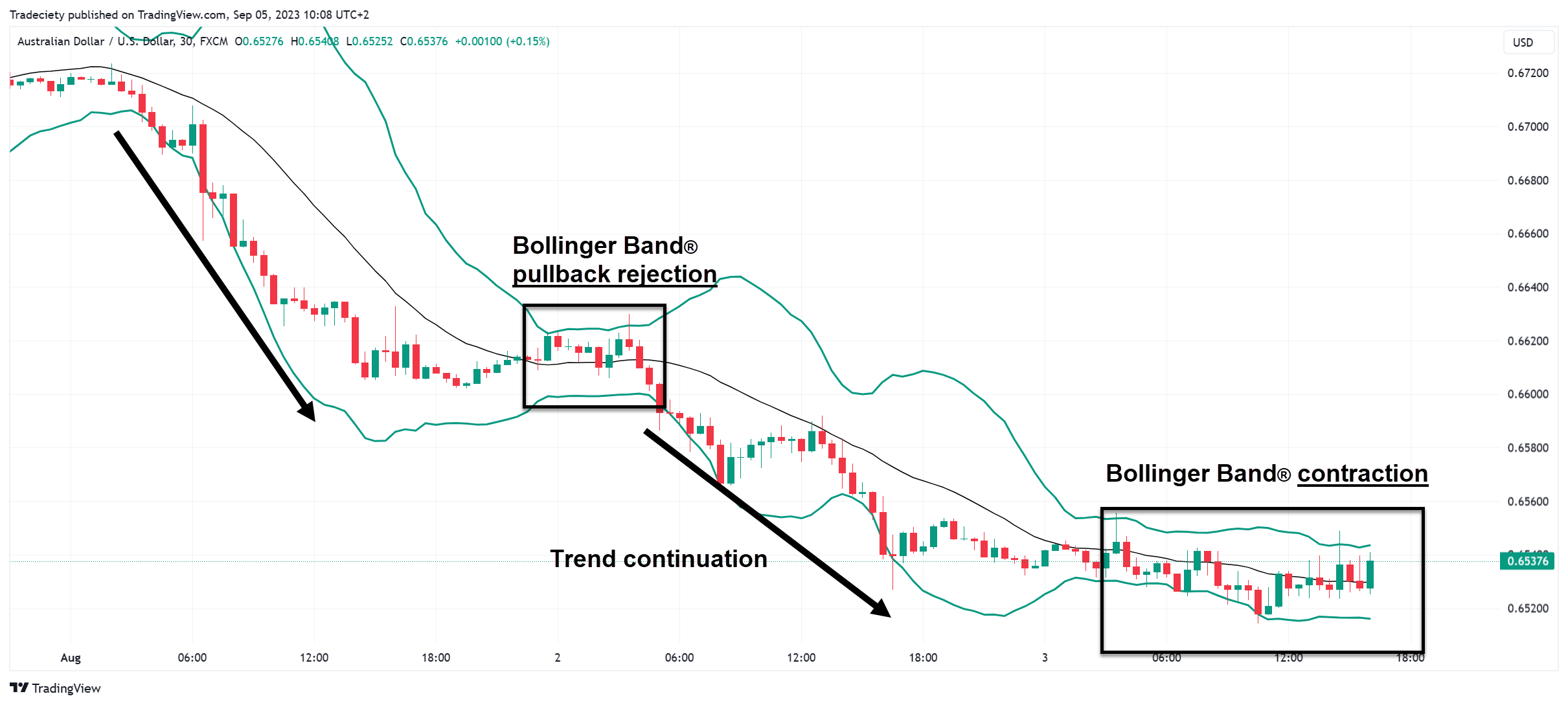
The screenshot below shows that the price is in an overall down-trending market phase because the price kept pushing into the lower bands. Now, the Bollinger Bands ® started narrowing and the price even reached the higher Bollinger Bands ®. The reaction around the higher band can tell us a lot about the market behavior. In this example, the market just briefly poked above the higher Bollinger Bands ® and then immediately was rejected. Such a quick rejection move can be seen as a rejection of the bullish buying attempt. If such a rejection is followed by a strong bearish candle, this sequence may foreshadow more selling to come.
As we can see, after the Bollinger Bands ® rejection, the price started moving back into the lower bands immediately and the downtrend continued. The quick rejection, followed by the strong bearish move was an ideal trend continuation signal.
Lastly, we can also use the Bollinger Bands ® for reversal trading. For that, we are going to examine the Bollinger Bands ® on the higher timeframe, the Daily.
On the Daily timeframe, we look for a price candle that spikes through the outer band but gets rejected immediately. The stronger the rejection, the better the signal is.
In the screenshot below, we also see that the spike occurs with a fakeout, a failing breakout above the last highs.
Although you would use the Bollinger Bands ® signal from the higher timeframe to time your trades on the lower timeframe away from the spike, we can see that the price did move lower on the higher timeframe after the spike.
Bollinger Bands ® spikes can be a great higher timeframe signal. Especially when combined with other confluence factors such as higher timeframe support and resistance levels and other exhaustion signals.
The Bollinger Bands ® indicator is a multi-purpose trading tool that can be used in many ways as we have learned throughout the article. Although the Bollinger Bands ® are classified as an indicator, the use of volatility and the concept of the standard deviation turn the Bollinger Bands ® indicator into an important price action trading tool.
The Bollinger Bands ® indicator is ideal for trend-following trading, and trend-continuation trading, and can even be used by reversal traders.
As always, we recommend trying the Bollinger Bands ® indicator in a backtest first before moving on to using it in your demo trading to evaluate its effectiveness and explore the different use cases of the indicator.
We have been trading supply and demand strategies for over ten years, and they have stood the test of time remarkably well. Supply and demand is...

3 min read
Choosing the right trading journal is essential for traders wanting to analyze performance, refine strategies, and improve consistency. In this...

3 min read
“95% of all traders fail” is the most commonly used trading related statistic around the internet. But no research paper exists that proves this...